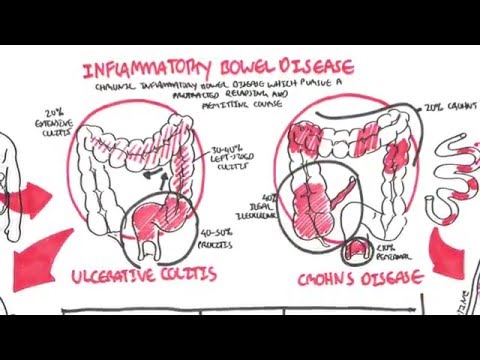
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD describes two kinds of bowel disorders ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The symptom of the two diseases includes diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and severe abdominal pain. In ulcerative, inflammation occurs only in the inner mucosa and starts from the anus and extends to the colon.
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that can occur at any place in the digestive tract. The symptom of the disease includes fatigue, severe diarrhea, and malnutrition and weight loss. Crohn's disease inflammation occurs in a different part of the digestive tract. The inflammation spread further to the layers of the bowel.
Studies show that there is a link between anxiety and IBD. Besides the physical symptoms, patients also experience psychological comorbidities. Most people with inflammatory bowel diseases are more likely to get depression or anxiety. Research shows that IBD patients were more likely to get depression and anxiety than the general public. The occurrence of anxiety was higher, especially for patients with Crohn's disease. IBD patients who get proper treatment are less likely to get anxiety.
Some factors can cause patients with IBD to develop psychological stress, anxiety disorder, surgery, poor socioeconomic status, active disease, and increasing age. Patients that are more likely to develop anxiety are those with an Ostomy. Patients with Ostomy have increased psychological problems and reduced quality of life. The disorder requires adequate treatment.
Depression and anxiety are linked to adverse clinical effects such as reduced quality of life, recurrent flares, and reduced adherence to treatment. Most IBD patients undergo surgery which may cause psychological stressors. Surgical-related stress may occur; this includes high caregiver burden, lost work time, financial security, and transforming body image.
What's Ostomy?
Ostomy is a surgery that leaves a permanent or temporal opening in the skin to remove body wastes. The surgical opening is created if the digestive system stops functioning due to an injury or disease.
The Effect of GI Disorders
IBD is a bowel disease and causes physiological effects on the body. The IBD patients also experience irritable bowel syndrome. Psychological symptoms mainly occur in individuals with functional GI disorders.
A patient can have both symptoms. Studies show that IBD patients were more likely to have at least one GI disorder, a common condition for patients with anxiety and IBD.
Treating Anxiety and IBD
Studies recommend physicians consider if the IBD patients also have a functional disorder. Physicians are advised to check the symptoms of the two conditions. They can also look for any symptoms or signs of inflammations and offer treatments.
If symptoms remain, it's an indication of a functional disorder, and the doctor should provide treatment for the condition. Most patients often avoid bringing up their psychological symptoms because of social stigma, and they end up untreated and undiagnosed for a long time.
Gastroenterologists, psychiatrists, psychologists, and other medical practitioners take care of IBD patients. If IBD patients are not attended to at the right time, the illness may lead to more disability. Individuals with IBD need to notify a physician to diagnose and treat the disease together with the existing anxiety disorder. The study recommends medical practitioners to use formal screening questionnaires to identify anxiety patients with IBD. Treatment of IBD patients should include therapy, medication for IBD, and anxiety.